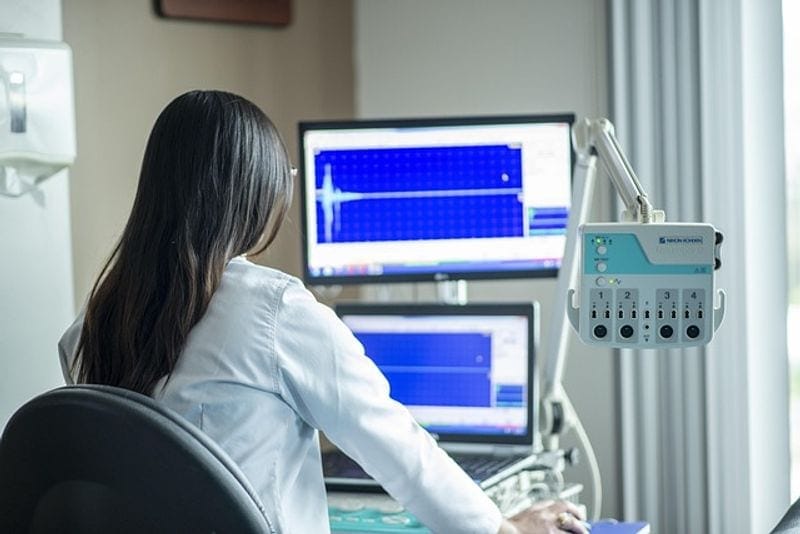
Videonystagmography, commonly known as VNG, is a non-invasive diagnostic test that plays a crucial role in identifying the underlying causes of dizziness, balance problems, and potential signs of a concussion. This specialized test utilizes infrared goggles to track and analyze the movements of the eyes, providing valuable insights into how the brain and inner ear coordinate to maintain balance and spatial orientation. By capturing and recording these eye movements, healthcare professionals can gain a deeper understanding of a patient’s vestibular function and make informed decisions regarding their diagnosis and treatment plan.
The process of VNG testing typically involves a series of eye movement tests that assess various aspects of vestibular function, such as gaze stability, nystagmus (involuntary eye movements), and positional vertigo. Patients undergoing a VNG test are required to wear specialized goggles equipped with infrared cameras that allow for precise tracking of eye movements during different head and body positions. These movements are then recorded and analyzed by a computer, generating valuable data that helps healthcare providers pinpoint any abnormalities or irregularities in the vestibular system.
VNG testing is a safe and effective procedure that is widely used in clinical settings to evaluate patients with symptoms of vertigo, imbalance, and other vestibular disorders. It provides valuable information that guides healthcare professionals in diagnosing conditions such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Meniere’s disease, and vestibular neuritis. If you want to learn more about VNG testing, you can visit Mount Sinai Health Library for additional resources and information.
The Science Behind VNG Testing
Videonystagmography (VNG) testing is based on the principle that eye movements are closely linked to the functioning of the vestibular system, which includes the inner ear and its connections to the brain. The technology behind VNG involves the use of infrared cameras integrated into specialized goggles worn by the patient during the test. These cameras track and record the movements of the eyes with high precision, capturing subtle changes in eye position and velocity that can provide valuable diagnostic information.
During a VNG test, the patient is guided through a series of eye movement exercises that stimulate different parts of the vestibular system. By analyzing the patterns and responses of the eyes to these stimuli, healthcare providers can assess the integrity and functionality of the patient’s vestibular system. Abnormalities in eye movements, such as nystagmus or gaze instability, can indicate underlying vestibular disorders or impairments in the brain-ear coordination.
One of the key advantages of VNG testing is its ability to objectively quantify and measure eye movements, allowing for more accurate assessments of vestibular function compared to traditional subjective tests. The data obtained from VNG tests can be analyzed in real-time or stored for further review, enabling healthcare providers to make evidence-based decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment strategies for patients with balance and dizziness issues. If you’re interested in learning more about the science behind VNG testing, you can explore additional resources at reputable healthcare websites.
Preparing for a VNG Test
Preparing for a Videonystagmography (VNG) test involves several steps to ensure accurate and reliable results. Before the test, it is essential to follow any pre-test instructions provided by your healthcare provider. These instructions may include avoiding certain medications that can affect vestibular function, such as anti-nausea drugs or sedatives, as well as refraining from consuming food or drinks that could impact the test results.

On the day of the VNG test, patients should wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing eye makeup or contact lenses, as these can interfere with the infrared cameras used to track eye movements. It is important to inform the healthcare provider about any existing medical conditions or concerns, as well as any recent changes in symptoms related to dizziness or balance issues.
During the VNG test, patients will be guided through a series of eye movement exercises that may involve tracking moving objects, focusing on stationary targets, or changing head positions to provoke specific vestibular responses. The duration of the test can vary depending on the complexity of the symptoms being assessed, but it typically lasts between 30 minutes to an hour.
After the VNG test is completed, the healthcare provider will review the results and discuss their findings with the patient. These results can provide valuable insights into the functioning of the vestibular system and aid in the diagnosis and management of various vestibular disorders. If you want to delve deeper into the preparation process for a VNG test, you can find additional resources at reputable healthcare websites.
What VNG Results Can Reveal
Interpreting the results of a Videonystagmography (VNG) test is a crucial step in understanding the patient’s vestibular function and identifying potential vestibular disorders. Healthcare providers analyze the data collected during the test to assess various parameters, such as the presence of nystagmus (involuntary eye movements), gaze stability, and the symmetry of eye movements between the two eyes. These findings help in determining the integrity of the vestibular system and identifying any abnormalities that may be contributing to the patient’s symptoms.
One of the key aspects of VNG test results is the characterization of nystagmus, which can provide valuable diagnostic information about the type and location of vestibular dysfunction. Different patterns of nystagmus, such as horizontal, vertical, or torsional movements, can indicate specific vestibular disorders or central nervous system abnormalities. Healthcare providers also look for any gaze-evoked nystagmus, which may suggest a peripheral vestibular pathology or central nervous system involvement.
Additionally, VNG test results can reveal abnormalities in smooth pursuit eye movements, saccades (rapid eye movements), and gaze stability during positional changes. These findings help healthcare providers assess the patient’s ability to maintain visual fixation and spatial orientation in response to different head and body positions. By interpreting these results in conjunction with the patient’s symptoms and medical history, healthcare providers can formulate an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan. To learn more about the significance of VNG test results, you can explore additional resources at reputable healthcare websites.
Applications of VNG in Healthcare
Videonystagmography (VNG) has diverse applications in healthcare, particularly in the diagnosis and management of various vestibular disorders and conditions related to balance and dizziness. One common condition that VNG can help diagnose is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), wherein specific head movements trigger brief episodes of vertigo due to dislodged inner ear crystals. By assessing the eye movements and positional responses of patients with BPPV, healthcare providers can confirm the diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment strategies, such as canalith repositioning maneuvers.
VNG testing is also valuable in evaluating patients with Meniere’s disease, a chronic inner ear disorder characterized by episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. By analyzing the vestibular function and nystagmus patterns observed during a VNG test, healthcare providers can differentiate between Meniere’s disease and other vestibular conditions, guiding the management of symptoms and potential treatment options.
Additionally, VNG can aid in diagnosing vestibular neuritis, an inflammation of the vestibular nerve that can cause sudden vertigo and imbalance. The findings from a VNG test, including spontaneous nystagmus and abnormalities in gaze stability, can help healthcare providers differentiate vestibular neuritis from other causes of vertigo and formulate a targeted treatment plan. Understanding the diverse applications of VNG in healthcare underscores its significance as a diagnostic tool for a wide range of vestibular disorders and conditions. For more information on the applications of VNG in healthcare, you can refer to authoritative healthcare resources available online.
Benefits and Limitations of VNG
Videonystagmography (VNG) offers several benefits as a diagnostic tool in assessing vestibular function and identifying vestibular disorders. One of the key advantages of VNG is its non-invasive nature, making it a safe and well-tolerated test for patients of various ages. The use of infrared goggles in VNG testing allows for precise and objective measurements of eye movements, providing healthcare providers with valuable data to analyze and interpret.
Furthermore, VNG testing offers real-time feedback on eye movements, enabling healthcare providers to observe and assess the vestibular function of patients during the test. This immediate feedback can aid in identifying abnormal eye movements, nystagmus patterns, or gaze instabilities that may indicate vestibular dysfunction. The ability to capture and analyze eye movements in different head and body positions enhances the diagnostic accuracy of VNG in detecting vestibular disorders.
Despite its advantages, VNG testing also has limitations that healthcare providers need to consider. Factors such as patient cooperation, underlying medical conditions, and medications can potentially influence the results of a VNG test. Additionally, interpreting VNG results requires specialized training and expertise to accurately diagnose vestibular disorders and differentiate between peripheral and central vestibular pathologies. Understanding the benefits and limitations of VNG testing is essential in optimizing its use as a diagnostic tool in evaluating patients with balance and dizziness issues. For more information on the benefits and limitations of VNG testing, you can explore relevant healthcare resources online.
Future Innovations in VNG Technology
The future of Videonystagmography (VNG) technology holds promising advancements that can further enhance its capabilities in diagnosing vestibular disorders and evaluating balance-related conditions. One area of innovation in VNG technology involves the development of more portable and user-friendly devices for conducting tests outside traditional clinical settings. These portable VNG systems aim to improve accessibility to vestibular testing and enable healthcare providers to assess patients in diverse environments.
Advancements in VNG technology also include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms for analyzing eye movements and interpreting test results more efficiently. AI-driven analysis of VNG data can help healthcare providers identify subtle abnormalities or patterns in eye movements that may be indicative of specific vestibular disorders. By automating certain aspects of VNG interpretation, AI-powered VNG systems have the potential to streamline the diagnostic process and improve the accuracy of results.
Moreover, researchers are exploring the integration of virtual reality (VR) technology in VNG testing to create more immersive and interactive testing environments for patients. By incorporating VR simulations into VNG assessments, healthcare providers can recreate challenging visual scenarios that may trigger vestibular symptoms in patients with certain disorders. This innovative approach to VNG testing aims to replicate real-world situations more accurately and provide a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s vestibular function. Stay informed about the latest advancements in VNG technology by exploring authoritative healthcare resources and staying updated on industry developments.